US utility-scale solar deployment is set to reach a record 22GW this year, with the technology accounting for almost half of the new generating capacity due to be added to the power grid from 2022 to 2023.
That is according to new figures from the country’s Energy Information Administration (EIA), which said a total of 85GW of new generating capacity is expected to be installed in the next two years, 41GW (48%) of which will be utility-scale solar.
Having installed 13GW of utility-scale solar in 2021, deployment is set to jump almost 70% this year to 22GW, with large additions likely to continue because of falling solar technology costs and the 2020 extension of the solar investment tax credit, the EIA said.
Utility-scale solar and battery storage projects together represent 51GW of new generating capacity planned for the next two years, 60% of the total additions.
More than half of the solar and battery storage capacity is to be installed in three states, with 12GW (23%) planned for Texas, 11GW (21%) in California and 4GW (7%) in New York.
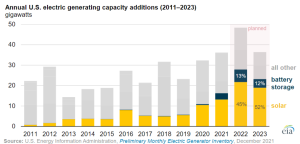 Image: EIA.
Image: EIA.
The EIA said declining costs, as well as favourable economics when deployed with renewables, have driven the expansion of battery storage, with 3.1GW of capacity added in 2021. In the next two years, an additional 10GW is due to be installed, more than 60% of which will be paired with solar projects.
Figures published last month from trade body the American Clean Power (ACP) Association put 2021 utility-scale solar deployment in the US at 12,364MW, taking the country’s total utility-scale solar capacity up to around 60.6GW.
Although 66GW of utility-scale PV is said to be under construction or in advanced development, ACP warned that supply chain challenges and trade barriers continue to threaten to significantly delay or even lead to the cancellation of projects, especially those unable to take delivery of modules due to product detainment at ports.






