Japan’s PV market growth has slowed since the feed-in tariff-driven boom of the mid-2010s, but the government considers solar an important aspect of the country’s ‘Green Transformation’, write analysts from Tokyo-based RTS PV.
The 2022 (January ~ December) Japanese annual PV market size is estimated to be 6.5GWDC, which is about the same volume as 2021, 0.8~1GW for residential, 5.5~5.7GW for non-residential PV installations.
Japan has moved from the FIT Act-based policies focusing on expansion of the installed capacity, deployed in the 2010s, to a new stage to simultaneously deploy the policies to integrate the power market and to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 46% in the 2020s.
As shown in Table 1, The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) clarified the position of PV as short-term measures and medium- to long-term measures based on the Basic Policy for the Realization of Green Transformation (GX) and will improve the business environment toward the maximum introduction of domestically produced renewable energy through reviewing and changing the existing schemes, regulations, and rules, while striving for establishing the next-generation network, securing the dispatching ability, and accelerating innovation.
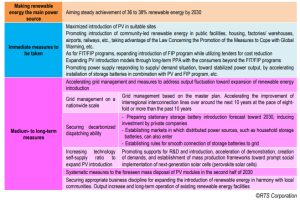 Table 1: Future deployment of PV introduction based on the Basic Policy for the Realization of GX. Image: RTS PV
Table 1: Future deployment of PV introduction based on the Basic Policy for the Realization of GX. Image: RTS PV
One of the measures to maximise the introduction of PV power generation in appropriate locations was announced on 31 January 2023 as the plan to distinguish rooftop installations from ground-mounted installations in purchase prices to promote rooftop installations, by utilising the rooftops of company buildings, factories and warehouses.
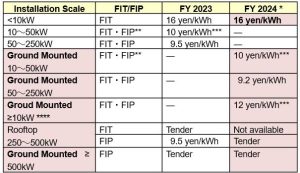 Table 2: New purchase price scheme for FY2024.
Table 2: New purchase price scheme for FY2024.
* From FY 2024 onward, the charge on the power producer side will be additionally taken into account. As for the FIT purchase price, tax-exclusive pricing shall be applied to taxable business operators and tax-inclusive pricing will be applied to tax-exempt business operators, in line with the planned introduction of the qualified invoice system.
** From FY 2023 onward, the FIP programme will be also applied to 10 – < 50 kW systems if they satisfy certain requirements
*** For 10 – < 50 kW PV systems, in principle, the requirements for self-consumption type PV systems for approving power sources as locally-used power sources will be applied
**** The FIT purchase price and FIP standard price of ≥ 10 kW systems for FY 2024 will be also applied to the second half of FY 2023 (October 2023 to March 2024)
On the other hand, power consumer group, including citizens and businesses, is more motivated than ever to introduce PV power generation against a backdrop of rising electricity prices, enhancing resilience and a stronger response to decarbonisation.
New business model for residential PV systems, a service with a third-party ownership (TOP) model in which PV systems and storage batteries are installed at no initial cost in cooperation with electric companies to promote ‘zero energy homes’ (ZEH) has launched and expanded.
In public and industrial applications, the introduction of PV systems on the roofs of factories and logistics facilities with PPA model has advanced, and not only on-site PPA but also off-site PPA initiatives have progressed, mainly by businesses that are members of RE100 or RE Action committed to 100% renewable electricity.
The PV industry must have a great opportunity as a key player to demonstrate the new advantages of PV power generation and significantly lower the hurdle for the introduction of PV power generation, and ultimately change the game for the power consumer group.
Moving from Feed-in-Tariff (FIT)-oriented introduction to PPA model will allow the power consumer group to free from raising funds to introduce PV power generation by shifting from “Yen/kW” to “Yen/kWh”.
Also, the transition from FIT programme to fixed unit price payment for PV power will free power consumers from the risk of higher electricity costs. A great opportunity has arrived in the PV industry, and 2023 must be the tipping point for new growth of the industry, working together with power consumers.
About the Author
RTS Corporation is a PV industry / market consulting company based in Tokyo, Japan. RTS has been supporting the growth of the PV industry for nearly 40 years, providing consulting services optimised for each client interested in the PV business.






