March 28, 2025, Japan New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization NEDO has formulated a new technology development guideline for the large-scale introduction of solar power generation, the “Photovoltaic Power Generation Development Strategy 2025 (NEDO PV Challenges 2025)”
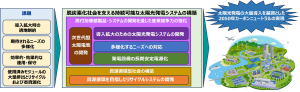
The Strategy summarizes the current situation and issues related to solar power generation both in Japan and overseas, and presents five technical measures to be addressed in the future: (1) development of next-generation solar cells, (2) development of solar power generation systems to expand introduction, (3) response to diversifying needs, (4) long-term stable power supply of power generation facilities, and (5) development of a recycling system aimed at resource circulation.
NEDO said it will also kick off its Solar Power Expansion and Technology Development Project in fiscal 2025 to support decarbonization efforts. This project will accelerate the transition to sustainable solar energy, as outlined in Japan’s 7th Basic Energy Plan, which was approved in February. The plan aims for renewables to account for 40% to 50% of Japan’s energy mix by 2040, with solar power contributing 23% to 29% of the total.
The organization said the new strategy builds on previous roadmaps such as PV2030 (2004), PV2030+ (2009), PV Challenges (2014), and PV Challenges 2020 (2020). It aims to address four key challenges identified for scaling up solar deployment: land constraints for large-scale installations, diverse market demands, long-term operational stability, and managing end-of-life modules through recycling.
NEDO’s technical initiatives will focus on developing next-generation solar cells, including high-efficiency technologies such as perovskite, tandem, and III-V compound cells to remain competitive globally.
To address these issues, The organization will promote the following five technological measures from two perspectives: development, mass introduction, and maintenance of solar power generation systems, to strengthen industrial competitiveness through the development of high-value-added products and systems; and manufacturing using fewer resources and reusing resources through recycling, etc., to build a resource-circulating society.
(1) Development of next-generation solar cells
The development of highly efficient solar cells, such as perovskite solar cells, tandem solar cells, and III-V compound solar cells, is a topic of intensifying global competition.
(2) Developing solar power generation systems to expand adoption
Development of solar power generation systems to reduce the total cost of power generation, including the development of modules suited to the installation location and installation and construction methods (flexible solar cells, etc.).
(3) Responding to Diversifying Needs
Development of solar cells for vehicles, demonstration tests to promote their installation, and development of technology to add functions (design as a building, color tone when installed on windows, etc.) that are expected to contribute to the expansion of the introduction of solar power generation systems.
(4) Providing stable, long-term power sources for power generation facilities
Development of efficient and effective operation and maintenance technologies for long-term stable operation, formulation and updating of safety guidelines for installation locations which are becoming increasingly common, as well as guidelines for new installation forms which are expected to be introduced more widely, and development of highly accurate solar radiation prediction technology.
(5) Development of recycling systems aimed at resource circulation
In addition to further reducing processing costs and developing separation and recycling technologies for new solar cell modules (perovskite solar cells, bifacial solar cell modules, etc.), we will also develop material recycling technologies for recovered materials.
NEDO plans to open public calls for projects under the Solar Power Expansion and Technology Development Project in mid-April.






