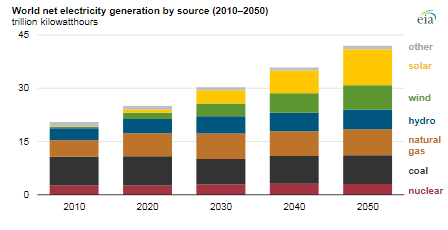
The Energy Information Administration projected that renewable resources—particularly solar and wind—will be the largest contributor to the growth in global electricity generation through 2050. It cautioned, however, that certain regions will still mainly use coal resources for electricity generation.
The projection are part of EIA’s International Energy Outlook 2021.
It said the absence of regional carbon policies or regulations along with rising natural gas prices after 2030—particularly in Asia and in regions that rely on higher-cost liquefied natural gas (LNG)—are likely to make coal the most economical generation fuel to pair with increased generation from wind and solar.
“This shift reverses the trend observed over recent decades,” EIA said. Although the cost of mining coal will likely raise coal prices after 2030, “we project that coal prices will remain low relative to natural gas prices and provide a cost-competitive option to natural gas-fired generation.”
Increases in coal-fired generation in Other non-OECD Asia—which includes Indonesia, Vietnam, and Thailand, among other countries—is forecast to account for over 75% of EIA’s projected increase in global coal-fired generation from 2030 to 2050. For other parts of non-OECD Asia, EIA projected that renewable energy sources would account for about 60% of the generation increase, primarily from wind and solar. Coal-fired generation will account for nearly all of the remaining growth, it said.
For Other non-OECD Asia, EIA projected that renewable energy sources will account for about 60% of the generation increase over the projection period, primarily from wind and solar. Coal-fired generation will account for nearly all of the remaining growth.
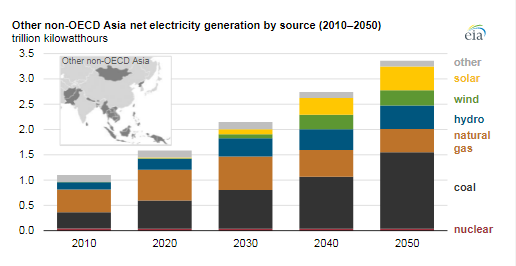
EIA said that Other non-OECD Asia is a geographically diverse region and that several countries in the region have limited domestic natural gas resources and have constrained access to natural gas pipelines and LNG regasification terminals.
EIA projected that in 2030, coal-fired generation will start displacing some natural gas-fired generation in Other non-OECD Asia because of abundant coal resources that can be competitively mined, natural gas prices that are projected to increase after 2030, and a lack of carbon policies or regulations in the region.
It said that coal-fired generation “will steadily increase” in Other non-OECD Asia through 2050; coal’s share of the region’s generation mix is projected to increase from 33% in 2020 to almost 50% in 2050.






