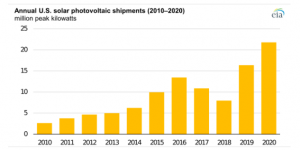
Solar photovoltaic (PV) module shipments in the United States, including imports, exports, domestic production, and sales touched a record high of 21.8 GW in 2020, 5.4 GW more than in 2019.
According to the Energy Information Administration (EIA), this translates to an increase of 33% year-on-year between 2019 and 2020.
Expiring solar tax credits, continued growth in utility-scale solar capacity and the falling costs for solar systems increased the shipments.
 In 2020, 89% of US solar PV module shipments were imported, totaling 19.3 GW, an increase of 26% compared to 15.3 GW of imports in 2019. Vietnam was the leading importer to the United States, followed by Malaysia, South Korea, and Thailand.
In 2020, 89% of US solar PV module shipments were imported, totaling 19.3 GW, an increase of 26% compared to 15.3 GW of imports in 2019. Vietnam was the leading importer to the United States, followed by Malaysia, South Korea, and Thailand.
Between 2019 and 2020, solar PV capacity additions in the United States increased by 25%, utility-scale solar capacity increased by 29%, and small-scale solar increased by 19%.
Meanwhile, the solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC) was supposed to reduce from 26% to 22% in 2020. Some of the solar capacity growth in 2020 resulted from a rush to get projects installed before the expected ITC decrease.
However, in December 2020, Congress passed an extension of the ITC, providing a 26% tax credit for solar systems installed from 2020 to 2022 and 22% for systems installed in 2023.
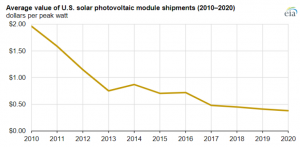
The cost of PV modules has declined significantly since 2010, helping drive the growth of solar PV module shipments, the supply chain for PV module components was disrupted a few times in 2020.
The average price of solar shipments decreased from $1.96/Wp in 2010 to $0.38/Wp in 2020. Lower supply chain costs and an oversupply of modules because of increased production are largely responsible for the declines in the average value of solar PV modules over the past decade.
 The US solar market has already surpassed 100 GW of installed power generating capacity, doubling the industry’s size over the last 3.5 years. In 2020, the US Solar Industry grew by 43%, with 19.2 GW Installed.
The US solar market has already surpassed 100 GW of installed power generating capacity, doubling the industry’s size over the last 3.5 years. In 2020, the US Solar Industry grew by 43%, with 19.2 GW Installed.
According to a report by National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), residential, commercial-rooftop, and utility-scale solar systems have witnessed a 64%, 69%, and 82% decline in costs since 2010, respectively, in the United States. The decline in costs of the residential, commercial, and utility-scale solar system was mainly due to increased module efficiency and lower inverter and hardware costs.
US Solar Photovoltaic Module Shipments Up 33% in 2020
In 2020, 89% of US solar PV modules were imported
Source:MERCOM
ViaArjun Joshi






